Introduction
Digital banking refers to the provision of banking services and the management of financial transactions through electronic channels and platforms. Primarily accessed via the internet or mobile devices. It encompasses a wide range of activities that allow customers to conduct banking activities remotely. Without the need to physically visit a bank branch. Digital banking includes services such as:
- Online Banking: Accessing and managing bank accounts through a secure website provided by the bank. This includes activities such as checking balances, transferring funds between accounts, paying bills, and viewing transaction history.
- Mobile Banking: Using mobile applications provided by banks to perform similar banking activities as online banking. But through smartphones or tablets. Mobile banking offers convenience and flexibility. Allowing customers to bank on the go.
- Mobile Payments: Making payments or transferring money using mobile devices. This can include peer-to-peer transfers, mobile wallets, and contactless payments using Near Field Communication (NFC) technology.
- Remote Deposit Capture: Depositing checks remotely by capturing an image of the check using a mobile device and submitting it through the bank’s mobile app or website.
- Digital Wallets: Storing payment card information securely on mobile devices to make digital payments. Digital wallets may also integrate loyalty programs, coupons, and other features.
- Automated Customer Service: Incorporating chatbots or virtual assistants to provide customer support, answer queries, and assist with basic banking tasks.
- Data Analytics and Personalization: Analyzing customer behavior and transaction patterns to offer personalized recommendations, financial advice, and targeted products or services.
- Security Features: Implementing various security measures. Such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and biometric authentication. To protect customer information and prevent fraud.
Banking Offers
Digital banking offers numerous benefits, including 24/7 accessibility, real-time transactions, streamlined account management, and enhanced convenience. It has transformed the way banking services are delivered, making transactions faster, more convenient, and more secure for customers.
Digital banking refers to the use of electronic channels, platforms, and technology to conduct various banking activities and services remotely, without the need for physical presence at a bank branch. It encompasses a wide range of services that can be accessed and managed online or through mobile devices, including:
- Online Banking: Customers can access their bank accounts, view balances, and transaction history, transfer funds between accounts, pay bills, and perform other banking activities through a secure website provided by their bank.
- Mobile Banking: Banks offer mobile apps that allow customers to perform similar banking activities as online banking, but through their smartphones or tablets. This provides greater convenience and flexibility, as customers can bank on the go.
- Mobile Payments: Digital banking facilitates various forms of mobile payments, such as peer-to-peer transfers, mobile wallets (e.g., Apple Pay, Google Pay), and contactless payments using Near Field Communication (NFC) technology.
- Digital Wallets: These are applications or platforms that allow users to store payment card information securely and make payments digitally. They can also integrate loyalty programs, coupons, and other features.
- Remote Deposit Capture: This feature enables customers to deposit checks remotely by capturing an image of the check using their mobile device and submitting it through the bank’s app or website.
- Automated Customer Service: Many digital banking platforms incorporate chatbots or virtual assistants to provide customer support, answer queries, and assist with basic banking tasks.
- Data Analytics and Personalization: Banks use data analytics to analyze customer behavior, preferences, and transaction patterns to offer personalized recommendations, financial advice, and targeted products or services.
- Security Features: Digital banking platforms employ various security measures, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and biometric authentication (e.g., fingerprint or facial recognition), to protect customer information and prevent fraud.
Digital Banking
Digital banking has become increasingly popular due to its convenience, accessibility, and efficiency. It offers customers the flexibility to manage their finances anytime, anywhere, and has transformed the way banking services are delivered, making transactions faster, more convenient, and more secure.
- Real-Time Transactions: Digital banking platforms often facilitate real-time transactions, allowing customers to see immediate updates to their account balances and transaction history. This provides greater transparency and helps users stay informed about their finances.
- 24/7 Access: Unlike traditional banking, which is typically limited to branch hours, digital banking services are available 24 hours a day, seven days a week. This flexibility allows customers to conduct banking activities at their convenience, even outside of regular business hours.
- Remote Account Opening: Many digital banks offer the ability to open new accounts entirely online, without the need to visit a physical branch. This streamlined process often involves digital identity verification and electronic document submission. Making it convenient for customers, especially those who may not have easy access to a local branch.
- Integration with Third-Party Services: Digital banking platforms may integrate with third-party financial management tools, investment platforms, or other fintech services, allowing customers to access a wider range of financial services and manage their entire financial portfolio from a single interface.
- Customizable Alerts and Notifications: Users can set up personalized alerts and notifications to stay informed about account activity, such as large transactions, low balances, or upcoming bill payments. This helps users monitor their finances more effectively and detect any suspicious or unauthorized transactions promptly.
- Paperless Transactions: Digital banking reduces reliance on paper-based transactions and documentation, leading to a more environmentally friendly and sustainable banking experience. Electronic statements, digital receipts, and online document storage minimize the need for physical paperwork.
- Financial Education and Tools: Many digital banking platforms offer educational resources, budgeting tools, and financial planning calculators to help users improve their financial literacy, set financial goals, and make more informed decisions about their money management.
- Global Accessibility: Digital banking transcends geographical boundaries, allowing customers to access their accounts and perform transactions from anywhere in the world with an internet connection. This is particularly beneficial for travelers and expatriates who need seamless access to banking services across different countries.
Overall, digital banking continues to evolve and innovate. Leveraging technology to enhance customer experience, improve efficiency. And expand the range of financial services available to users. As technology advances further.
Mobile Financial Services
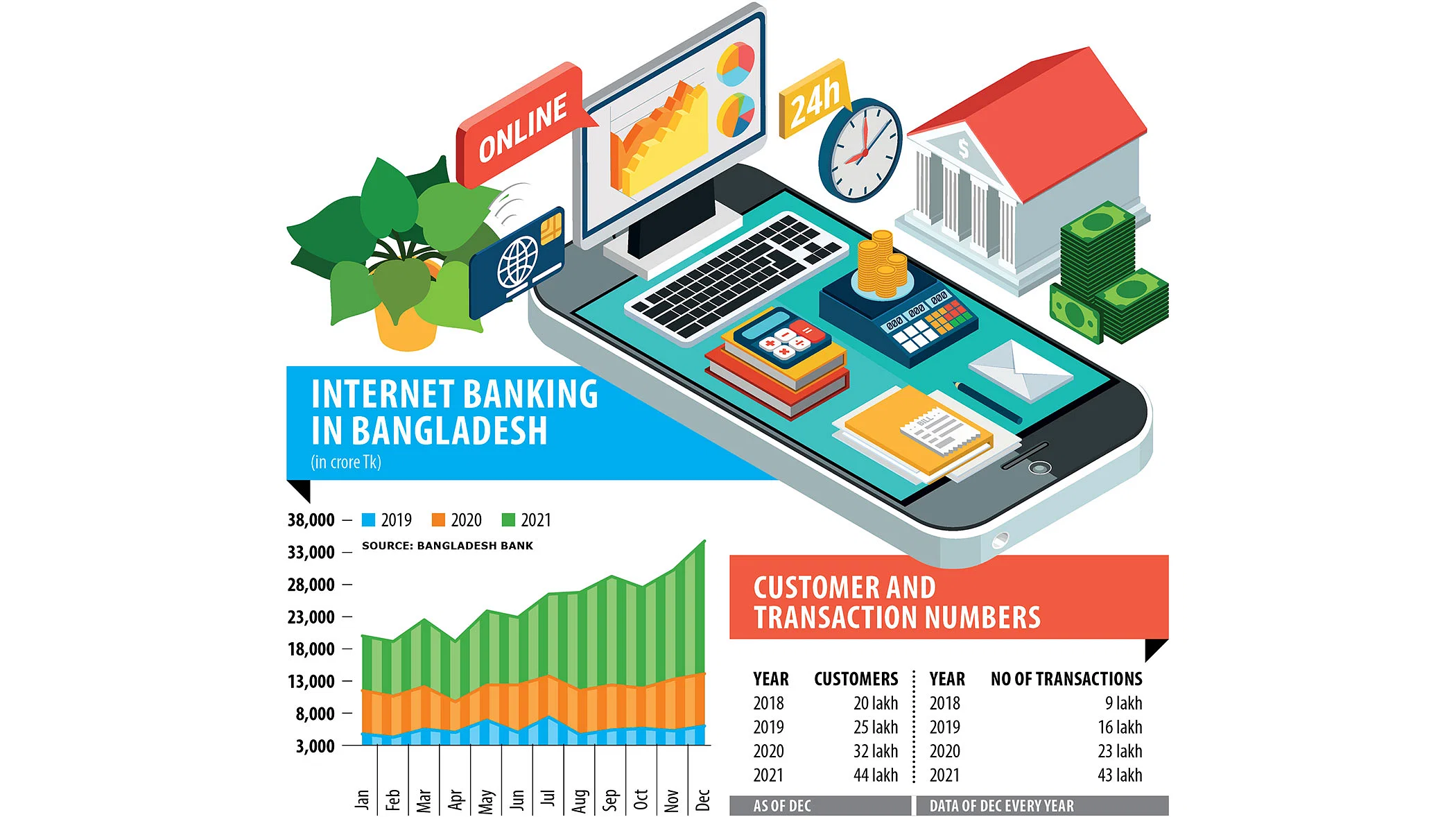
Digital banking in Bangladesh has experienced significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by advancements in technology, increasing internet penetration, and the government’s push towards a digital economy. Here are some key aspects of digital banking in Bangladesh:
- Mobile Financial Services (MFS): Bangladesh has seen widespread adoption of mobile financial services. With platforms like bKash, Nagad, Rocket, and others leading the way. These services allow users to perform various financial transactions. Including money transfers, bill payments, airtime top-ups, and more, using their mobile phones.
- Online Banking: Traditional banks in Bangladesh have also introduced online banking platforms. Allowing customers to access their accounts, transfer funds, pay bills, and perform other banking activities through the internet. Many banks offer mobile apps for added convenience.
- Agent Banking: Agent banking has played a crucial role in expanding financial inclusion in Bangladesh. Agents act as intermediaries. Providing basic banking services on behalf of banks using point-of-sale (POS) devices or mobile apps.
- Government Initiatives: The Bangladesh government has launched various initiatives to promote digital banking and financial inclusion. For example, the Digital Bangladesh initiative aims to leverage technology to improve public services. Including financial services.
- Partnerships and Collaboration: Fintech startups and established banks often collaborate to innovate and expand digital banking services. These partnerships have led to the development of new financial products. Such as digital loans, savings accounts, and insurance services. Tailored to the needs of different customer segments.
- Security and Regulatory Framework: With the growth of digital banking comes the need for robust cybersecurity measures and regulatory oversight. The Bangladesh Bank, the country’s central bank. Has introduced regulations and guidelines to ensure the security of digital transactions and protect consumers’ interests.
- Challenges: Despite the progress, digital banking in Bangladesh faces challenges such as low financial literacy. Inadequate infrastructure in rural areas, and concerns about cybersecurity and data privacy.
Overall, digital banking in Bangladesh holds immense potential to drive financial inclusion, boost economic growth. And improve the efficiency of financial services delivery. Continued investment in technology, infrastructure. And regulatory frameworks will be crucial for realizing this potential and ensuring that digital banking benefits all segments of society.